Bear market: definition, types and trading strategies
The situation on the financial markets depends on many factors and can change very quickly. A trader must react to these changes correctly, be able to adapt and competently build his trading strategy. It will help him to save and increase the capital even in the period of market instability.
In this article we explain the definition of a bear market and tell about the trading strategies, which can be used to make profit during a market downturn.
Definition and types of bear markets
A bear market is a decrease in asset prices over an extended period of time. The main indicator of a bear market is a decrease in one of the major indexes (e.g., S&P 500, NASDAQ 100, Dow Jones) by 20% or more from their last high price.
It should not be confused with a price correction in the market, when after a prolonged rise the value drops by 10-15% and then flattens out again.
Let’s look at the three main types of bear markets.
1. Cyclical. They are observed with high inflation during economic downturns, when large enterprises massively reduce expenditures and investments. Cyclical bear markets are characterized by a gradual decline in prices and duration of 1 to 2 years.
2. Structural. These bear markets are caused by long-term worsening in the global economy and global banking crises. For example, a structural bear market was observed during the global crisis from 2007 to 2009. This type of bear market lasts longer than the others, averaging 2 to 4 years, and recovery from it can take up to 10 years.
3. Event-driven. They depend on global events that significantly affect the economy: epidemics, wars, natural disasters. Event-driven bear markets tend to have the smallest price decreases and last from several weeks to several months.
Determining the type of bear market is an important step in creating a trading strategy. The trader needs to predict the duration of the bear phase and properly assess investment risks.
Trading strategies on the bear market
Trading on a bear market implies stress tolerance, because it is characterized by high volatility. The trader must calmly react to the rapid market changes and make reasonable decisions, not based on fears and emotions.
We will look at popular bear market trading strategies, which traders use to save capital.
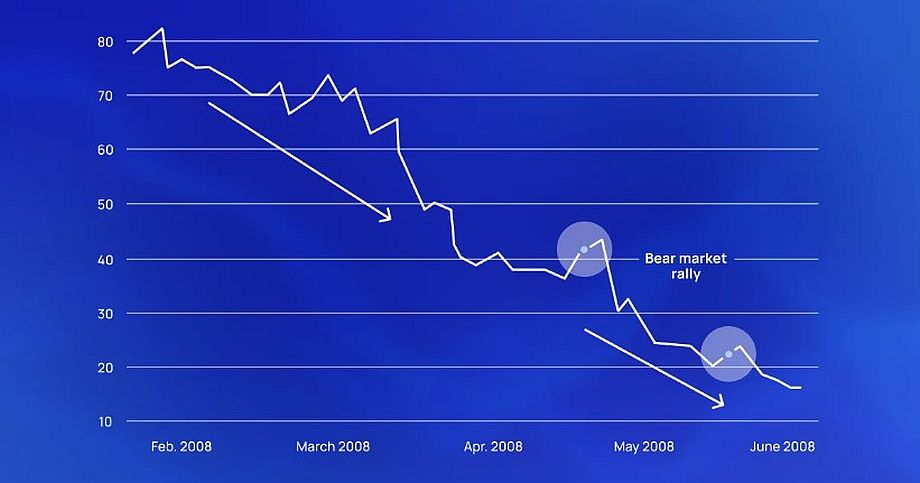
Bear market rally
During a prolonged bear market, there can be a temporary increase in asset prices – a stock market rally. Expert traders anticipate this phenomenon by analyzing indicators, and buy assets when prices are still decreasing.
A rally is an effective stock trading strategy on a bear market. But it is important for the trader to remember that the global downtrend continues and soon the price will turn down again. Therefore, the right exit point has a key role in this trading strategy.
Derivatives
Derivatives on the currency market are financial contracts concluded between the seller and the buyer. Their value is based on underlying assets such as stocks, bonds, and indexes. With derivatives, sellers (bears) can open short positions and profit from a decrease in the price of the underlying asset.
Popular for this trading strategy are CFDs, which allow trading not in the asset itself, but in the difference in its price at the moment of opening and closing of the transaction. CFD trading on short positions on the bear market is also used for hedging – risk management.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit orders
Orders on the currency market are orders to open and close a trader’s deal at a certain point on the price chart. They help control the size of profits and losses in a volatile bear market, where the situation can change quickly.
Stop-Loss is a type of order, through which the trader sets the maximum allowable level of losses of the transaction, after reaching which it is closed.
Take-Profit is an order, which automatically closes the transaction, if the profit from it has reached the rate set by the trader. Such order helps to fix profits during the rally at the bear market and trade short positions before the price turns in the opposite direction.
Conclusion – Bear markets
Trading on a bear market requires more detailed analysis and risk management than on a bull market. A trader must carefully assess the current situation and make quick decisions, because the classic speculative model “buy low – sell high” will not work in this situation.
It is important for a trader to create a trading strategy, combine different analytical instruments and not to be emotional, because it is possible to react to false signals and get a loss. Trading on this market is not suitable for everyone, but by following the right strategy, a trader can save and increase his capital even in times of global financial instability.