How to protect cryptocurrency
The basics of cryptosecurity
According to analytics company Chainalysis, in 2021, fraudsters seized $7.7 billion worth of cryptocurrencies, 81% more than in 2020. Scammers use a variety of methods to steal users’ assets, which beginners often fall for. How to protect your cryptocurrency? If you are just starting your journey into cryptocurrency, you should remember that cryptocurrency transactions, unlike fiat ones, are irreversible. In addition, due to the lack of a clear regulatory system, it’s very difficult to find fraudsters and bring them to justice.
In this article, we talk about the best ways to protect your cryptocurrency, as well as we take apart the most common mistakes of cryptocurrency security novices.
Security issues in the crypto world
As cryptocurrencies grow in popularity, so do the various fraudulent schemes that harm users. According to statistics, nearly $3 billion has been stolen from cryptocurrency exchanges since 2012, and hackers have launched numerous attacks on various cryptocurrency storage and purchase services since the Covid-19 pandemic began.
To get their hands on the funds, hackers can use a variety of methods, from stealing user passwords to hacking cryptocurrency platforms, as well as phishing attacks, where users provide their own data to fraudsters.
One of the most common fraud schemes is the theft of cryptocurrencies private keys. For example, in September 2020, hackers broke into the KuCoin exchange, which caused the loss of about $275 million in digital currency assets. The reason for the hack was the leakage of private keys to the exchange’s hot wallets.
Let us say right away that it is impossible to be 100% protected from hacks, but every investor can and should considerably minimize the risks. We have prepared 9 rules to take as a basis if you own or want to invest in cryptocurrency.
1. Buy cryptocurrency safely
In 2022, buying cryptocurrency is not a difficult task. It can be done on centralized and decentralized exchanges, cryptocurrency ATMs, and P2P platforms. But it is the great abundance of platforms that creates a problem, because before choosing a particular solution, it is necessary to do research and find out what kind of security the chosen platform provides. There are many resources on the Internet that list when and which exchanges have been hacked. Study these lists and see what security measures are maintained by the exchanges.
On centralized exchanges, security is ensured through enhanced regulation, as well as KYC and AML procedures. If full decentralization is important and you decide to use DEX, look for a platform audit by an independent auditor.
If you choose P2P, pay attention to whether the platform conducts KYC and AML procedures. Great if the P2P platform has an escrow system. That is, once a transaction is opened, the amount listed in the ad is transferred from the seller’s account to the escrow account. If the seller tries to cheat you, you can get your funds back.
2. Don’t buy cryptocurrency for cash
You can often see ads for buying cryptocurrency for cash. That is, one user sends another user a cryptocurrency and gets cash for it. In such a case, P2P platforms cannot regulate the transaction and ensure its security.
A face-to-face meeting to transfer the cash may not take place and there is a chance that the trading partner will turn out to be a scammer and run away after receiving the funds.
The way out of such situation is to buy cryptocurrency on proven platforms with system of protection of user’s funds.
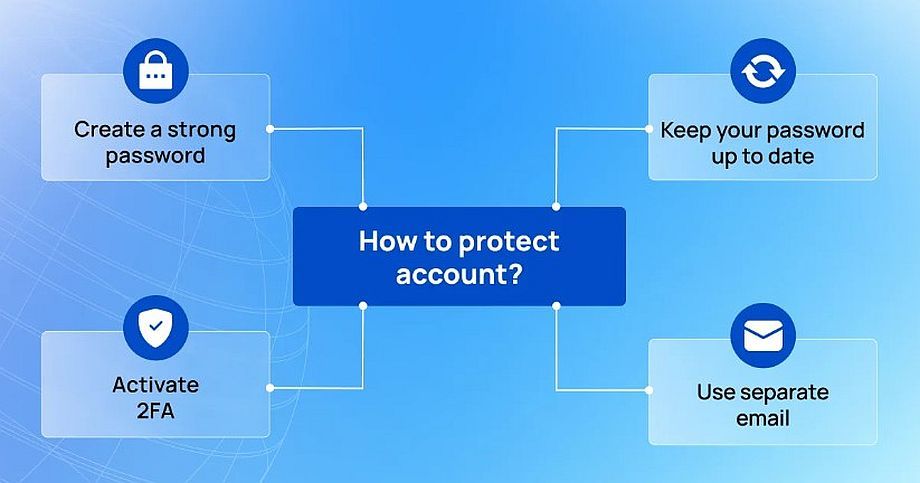
3. Set maximum account protection
After registering on any cryptoplatform, use all available methods to protect your account.
– Create a strong password and update it regularly
According to a 2022 survey, 61% of users said they use the same password on several or even all the sites they use. And only 11.9% of those surveyed are confident that their passwords are secure.
If you want to protect your cryptocurrency and keep it safe, be sure to use a unique password that is at least 8 characters long and contains numbers, capital letters. It is not recommended to add personal information, such as your date of birth, to your password. In addition, do not forget to change your password regularly. The optimal period is every month.
And one more important rule is to keep your passwords in special password managers like LastPass and 1Password. It is not recommended to store your passwords in a browser. According to statistics, only 1 out of 4 respondents used a password manager to store their crypto-wallet password there.
– Two-Factor Authentication Activation (2FA)
Two-factor authentication is an additional level of account protection in case your password is compromised. If 2FA is activated, in addition to the password, the user has to enter a code that comes to the phone, email, or telegram bot. In addition, on crypto platforms, two-factor authentication is activated not only when logging into an account, but also when making transactions.
– Use a separate email
Make a special email for financial personal accounts and don’t use it on other sites.
4. Don’t keep all your assets in one wallet
There are two categories of cryptocurrency wallets — hot and cold. The former have a permanent connection to the network, and the latter work offline. The best option is to use both hot and cold wallets to store assets. On a hot wallet, it’s convenient to store a small amount of assets on a hot wallet that you can access at any time. It is convenient to store large amounts of assets in a cold wallet because the security of such wallets is higher.
A hardware wallet has no connection to the Internet, so it is extremely difficult for an attacker to infect it with malware.
When you make a transaction with a hardware wallet, you need to connect it to your computer or mobile device via USB or Bluetooth. A signature is created inside the wallet and sent to your Internet-connected device, allowing you to complete transactions without revealing your key to a device that may be infected with malware.
Hardware wallets also have PINs, so it would still be difficult for an attacker to get your cryptocurrency if your wallet is physically stolen.
You can learn more about the characteristics of hot and cold wallets here.
5. Keep your private keys and SEED phrase in a safe place
A private key is an alphanumeric code, which you can use to access your wallet. A SEED phrase is a set of words used to back up your wallet and restore access to your wallet if you lose your device.
Many cryptocurrency newbies make the mistake of storing the private key and SEED phrase in the cloud, which can be hacked by fraudsters. To avoid hacking, it is recommended that you store your private key and SEED phrase on a piece of paper and keep it in a safe place.
6. Do not open suspicious links
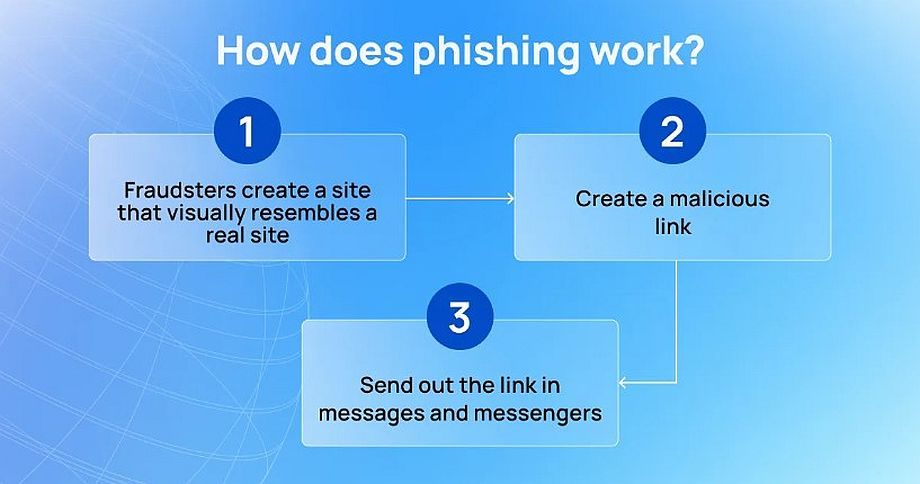
Phishing is an attack in which attackers impersonate an official resource or even a user they know in order to obtain confidential information by sending a malicious link. It can be contained in an email or website, as well as in a personal message.
When a user clicks on such a link, the malicious program gets on his or her computer, collects data and passes it to phishers.
To avoid phishing, never follow any suspicious links sent to you in messages, and don’t log in to your account at the exchange, if you’re not sure that you are on the official site. In addition, only download software from official sources and install protective software such as antivirus or a firewall.
Another way to protect yourself from phishing, even if you opened a malicious link, is to use another computer for your cryptocurrency transactions. That is, check your email on one device that has no cryptocurrency wallet or other data on it, and perform transactions on another.
7. Beware of scam projects
In addition to hacking private keys and phishing attacks, cybercriminals often create scam projects in order to obtain funds from investors and then shut them down.
Let’s look at some examples of scam projects.
– Fake exchanges
Fraudsters can create copies of famous exchangers’ sites to get the user’s data they enter when logging into an account. Scammers then use the username and password entered by the user and use it on the real platform. A fake exchange can be identified by the lack of a secure HTTPS connection and typos in the address bar. In addition, fraudulent platforms often have an ill-conceived design and a lot of spelling and punctuation errors in the text.
– Fake exchangers
Sites that look like real online exchangers consist of several pages and offer users to exchange cryptocurrency for fiat. As a result, the user sends their cryptocurrency, but does not receive fiat for it. It is quite easy to recognize such a site due to the large number of negative reviews, unrealistic exchange rates, as well as the lack of technical support.
– Short-term projects
In this case, you invest money, attract new users who also invest money. The investment is recouped by each new user, but at the end the scheme either collapses or its creators disappear with the depositors’ money.
– Counterfeit Coins
As with fiat, cryptocurrencies can also be “faked”. You can’t copy someone’s bitcoins, but you can create a new fake coin and make money on investments from users.
Therefore, if you are attracted to some project, carefully study the information about it on all official resources and check the activity for signs of potential fraud.
8. Check the recipient’s wallet address
If you enter the wallet address manually, there’s a big risk of making a mistake and sending funds to the wrong recipient or to a non-existent address. And if in the second case, funds in a couple of days will return to the sender, in the first — the assets will be lost forever.
To avoid this kind of trouble, copy the recipient’s address or scan the QR-code, which completely minimizes the risk of entering the wrong address.
9. Don’t connect to public Wi-Fi
Very often we allow ourselves to connect to public Wi-Fi in parks, cafés, co-working spaces or restaurants. But when performing cryptocurrency transactions, you should avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi.
When using public Wi-Fi, scammers can easily intercept your Internet traffic and get information about your online activities and determine if you’re visiting cryptocurrency sites. In some cases, they can even view your transactions.
This won’t necessarily allow them to steal your cryptocurrency, but the scammer may decide to give you much more attention if they see you making high-value cryptocurrency transactions or just browsing cryptocurrency sites. This may not be the attention you need.
The optimal solution is not to connect to public Wi-Fi, but if there is no other option, you can install a VPN. It masks your IP address, encrypts messages and hides your online activities from hackers.
Summary
Security in the field of cryptocurrencies is the most important component, as we are talking about large sums that can be lost irretrievably. Keep in mind the main rules that we have pointed out and trade cryptocurrency safely. Protect your Cryptocurrency.