Public & Private Blockchains
Blockchain is a distributed registry that records information about every transaction of network users. In other words, it is a modern database that provides users with anonymity, transparency, and security.
Earlier, we told you what blockchain is and its types: public and private. Today, we’ll take a closer look at these types of blockchain, as well as their key differences from each other.
Public Blockchain: Definition and Benefits
Public blockchain is a completely open and transparent network that can be accessed by anyone. The main principles of public blockchain are decentralization, transparency, and equity. This means that the blockchain has no supervisory authority and all participants are equal. Every user of a public blockchain network can view information about transactions, transfers, and agreements, as well as participate in the consensus process (which blocks will be added to the network).
In addition, the public blockchain is immutable. That is, users can only add new entries, but it is not possible to change the data once the blocks have been verified.
The most popular public blockchains are Bitcoin and Ethereum. Bitcoin’s blockchain is used as a means of payment and investment, while Ethereum allows you to run smart contracts and decentralized applications based on its blockchain.
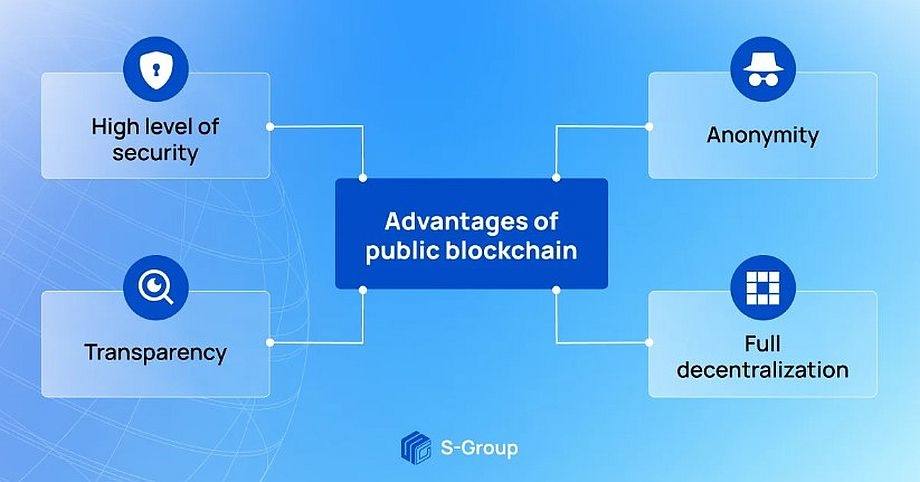
Advantages of public blockchain
The main advantages of public blockchain are considered to be: high security, transparency, anonymity and complete decentralization. Let’s take a closer look at each of these benefits.
1. High level of security
Transactions in the blockchain cannot be changed or deleted, and any changes must be voted on by all participants in the blockchain and only after consensus is reached will changes be accepted. In addition, both any changes and the validity of a transaction are recognized only if a majority of participants agree. This property makes the public blockchain immune to external interference.
Another aspect of the high security of a public blockchain is the large number of participants, because the more users, the harder it is for hackers to band together and hack into the network.
2. Transparency
Because public blockchains are created using open-source computational code, transactions are completely transparent and anyone can check them. Thus, there is no room for corruption or any other attempts to defraud the community in a public blockchain.
3. Anonymity
Although all transactions are visible to users, transaction details, sender and recipient details are not displayed. This means that it is impossible to trace the transaction back to the original address of the users.
4. Complete decentralization
Public blockchains have no centralized management facility, and transaction information is stored on the computers of all network participants. Users have equal rights within the network and can all manage the blockchain.
Private blockchain: definition and benefits
A private blockchain is a closed network that can only be accessed by an invitation from a central governing body, which can be either a single individual user or a group of individuals with rights. In a private blockchain, only a limited number of participants can make changes, configure rights, allocate access levels and agree on the addition of new users.
Most often, private blockchains are used by companies where complete confidentiality is important because only management can assign rights to users and grant access to information.
Because the private blockchain is managed by a specific set of people, some critics deny its decentralization and refer to it simply as a centralized database. Yes, there are similarities, but the private blockchain also has a number of similarities to the public decentralized blockchain.
– Immutability. Once data enters the blockchain, it becomes available to each participant and cannot be changed.
– Digital signatures. They make the transaction easier for the two parties because there is no need to involve intermediaries and lawyers.
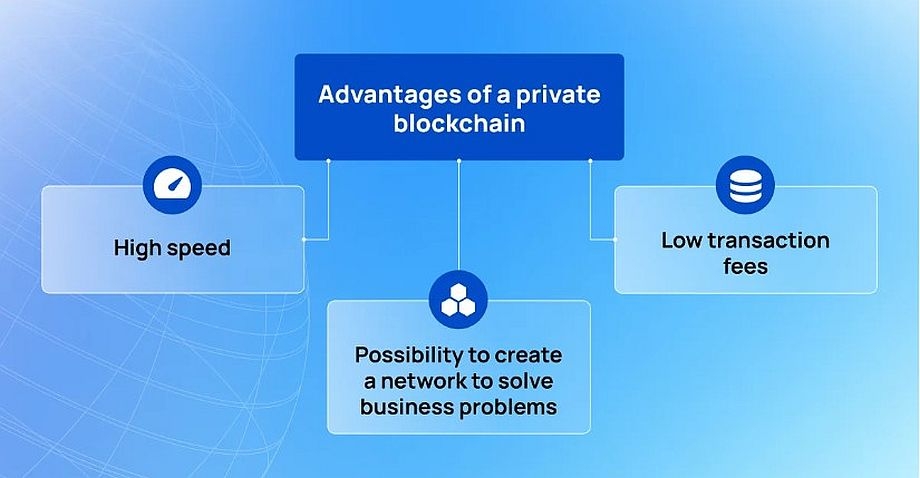
Benefits of private blockchain
Some of the main advantages of private blockchain include high speed, low transaction fees, and the ability to build a network to solve specific business problems.
1. High speed of operation
All processes in private blockchains run faster than in public blockchains because there are fewer computers in the blockchain and fewer users connected to the network. Consequently, information does not need to be transferred to thousands of computers at the same time, which loads the network and takes time.
2. Low transaction fees
On private blockchain platforms, transaction fees are extremely low. Unlike public blockchains, transaction fees do not increase depending on the number of requests, because there are far fewer participants in the network.
3. Ability to build a network to solve business problems
Using a private blockchain can help companies simplify auditing, accounting, and confidential project management. In fact, you can create a private blockchain for any business task and be confident that the information is secure.
The disadvantages of a private blockchain include a lower level of security. Due to the fact that a private network is managed by several people, it is much easier for hackers to hack into it and gain access to information, change it or delete it.
Comparing private and public blockchains
To summarize the information about the private and public blockchain, we present you with a comparison table with the key characteristics of these two networks.
Which type of blockchain to choose?
Both private and public blockchains have their advantages for use, depending on the specific purpose. If you need a blockchain to store sensitive information with access to a limited number of people, a private blockchain is the way to go. If full decentralization and security of your data is your primary concern, a public blockchain is the way to go.