Blockchain technology
Blockchain is a popular concept that everyone “hears about”, but not everyone can understand exactly what blockchain is, why it is needed, and where it is used.
The topic of blockchain and the answers to the questions above is the subject of a new article on our blog.
Blockchain Technology: Definition and History
Blockchain is a continuous chain of blocks that stores information about the transactions of all users. In simple words, blockchain is a modern database. Blockchain technology.
Blockchain is decentralized.
This means that information is stored simultaneously by all users of the network without a single registry, ensuring maximum invulnerability. Even if one or more computers are hacked, the information on the network is not lost.
In addition, the blockchain is immutable.
This means that users of the network can only add new information, but it is not possible to delete or change existing information. This effect is achieved through cryptography. Each record (block) is linked to a previous record (block) and contains a unique hash (alphanumeric code).
That is, if information in a block changes, the hash of the block changes too. And since this hash is included in the next block, the next block also changes. As a result, because of one small change, the data in the whole network changes. Therefore, no one user can change any information without everyone noticing.
History of Blockchain
Blockchain technology was first mentioned back in 1991, when research scientists Stuart Haber and Scott Stornett described the idea of a cryptographically secure blockchain. The scientists wanted to create a system in which the temporal values of documents could not be altered or corrupted.
Blockchain technology in cryptocurrency and as we know it now appeared in 2008, when a technical paper (white paper) describing blockchain technology was published by a person, or group of people, under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. And in 2009, the first blockchain was implemented as a public ledger of bitcoin transactions.
In 2014, blockchain 2.0 emerged, referring to applications beyond cryptocurrency. The Ethereum blockchain system introduces computer algorithms, known as smart contracts, into blocks.
Principle of blockchain and transactions within the network
The basis of cryptocurrency blockchains is SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm), or a secure hash algorithm that hashes the data received. If users enter the same information, the hash remains unchanged; if users enter different information, the hash automatically changes.
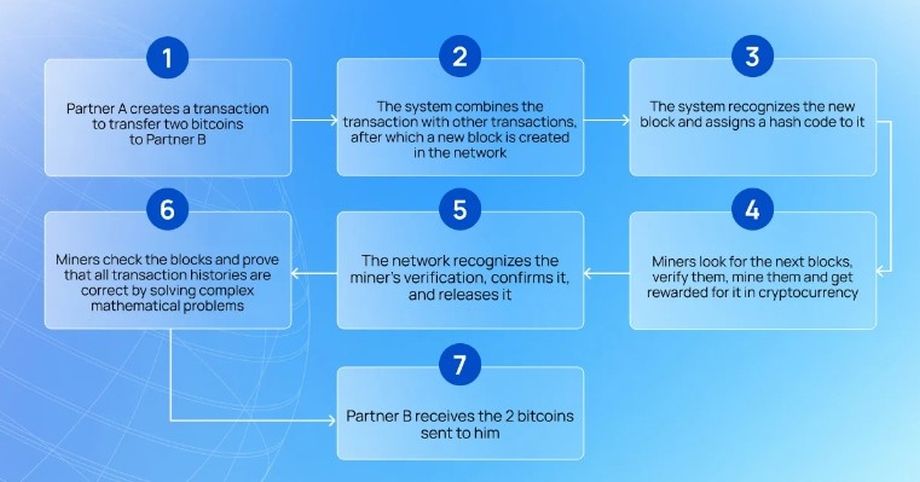
Let’s explain with an example how blockchain transactions work.
- Partner A wants to transfer 2 bitcoins to partner B and creates a transfer transaction.
- The system combines the transaction with other transactions and then creates a new block in the network.
- The system recognizes the new block and assigns it a unique hash code for identification.
- now the miners come into play — network members who check the blocks and prove that all transaction histories are correct, by solving complex mathematical problems.
- The network recognizes the miner’s verification, confirms it, and releases it.
- Miners look for the next blocks, verify them, mine them and get rewarded for it in cryptocurrency.
- Partner B receives the 2 bitcoins sent to him.
How the block verification process takes place
The process of verification of blocks by miners takes place on the consensus algorithm PoW (Proof Of Work) or proof of work done. In this case miners compete with each other in computing power and solve complex mathematical problems to mine a block. That is, miners with powerful computing equipment have more chances to decrypt a hash and get a reward for the block. The power of the equipment directly affects the number of hashes that a miner can calculate per second and the profit he will receive. That is, the more powerful the equipment, the more coins the miner gets.
Blockchain technology
Types of blockchain networks
There are three types of blockchain networks: private, public and hybrid. Let’s take a closer look at each of them.
Private blockchain
Available only to a limited number of users, and can only be connected subject to certain rules and restrictions. Private blockchain networks lack decentralization, so a certain circle of users can independently set up access rights for other network participants. It is because of the lack of decentralization that private blockchains are criticized by the cryptocurrency community.
Public Blockchain
An open and decentralized blockchain in which all users are equal and transactions are accessible and transparent.
Hybrid blockchain
A hybrid blockchain network combines the properties of a private and public blockchain. With such a blockchain, you can preserve the security of the public network and the privacy of the private one.
Advantages and disadvantages of blockchains
Let’s start with the advantages
– Distribution. Data is stored simultaneously by all users on thousands of devices. Therefore, the whole system and the data in it are resistant to failures and attacks.
– Stability. Confirmed requests are almost never cancelled, so it’s impossible to delete or change data on the blockchain.
– No middleman. Banking financial systems have an intermediary in the form of a bank, provider, or card issuer. In blockchain technology, there is no intermediary, which means there is no risk associated with trusting a certain organization.
– Of the disadvantages of blockchain, there is a 51% risk of attack. To change the data in the blockchain, a miner needs to convince everyone else that his version of the blockchain is correct. That means he needs more than 50% of all the power to do so. This is what the term “attack 51” stands for. It means a situation where a person or organization with 51% of the power can completely change the current blockchain.
But, conducting a 51% attack is still only in theory, because there has never been a single such case in the entire existence of blockchain.
Blockchain’s Technology Potential
Blockchain technology is penetrating people’s daily lives more and more every day. And while the technology is most actively used in the crypto world right now, blockchain’s potential doesn’t stop there. Blockchain technology is already beginning to be used in banking, healthcare, gaming, government, and digital identity.
In fact, blockchain technology can be used wherever you need to store and transmit data openly and transparently, and you can be sure that everyone who works with that data is honest.